上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理New England Biolabs(NEB)酶试剂全线产品,欢迎访问官网了解更多产品信息和订购。
产品信息
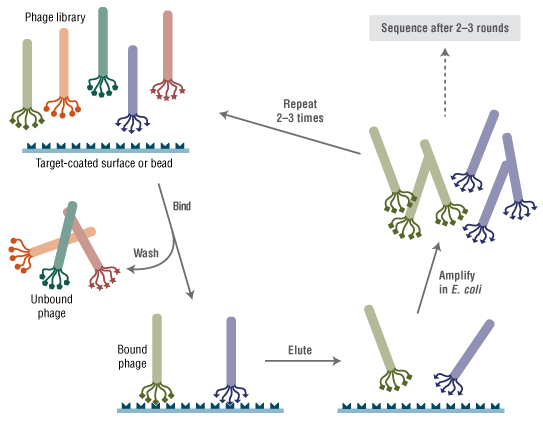
Ph.D.-12 噬菌体展示肽库试剂盒 v2 的制备原理是将随机十二肽组合库融合表达于 M13 噬菌体次要外壳蛋白(pIII)的 N 端(5-9)。这种肽后跟随一个直接位于野生型 pIII 序列之前的短间隔序列(Gly-Gly-Gly)。该库包含约 10 亿个电穿孔序列,在提供的 10 μl 噬菌体中经扩增一次,每个序列即可产生约 100 个拷贝。
展示肽形式:X12-GGG-野生型 M13 pIII
- 产品类别:
- Protein Tools Products,
- Phage Display Products
- 应用:
- Protein Analysis Tools,
- Phage Display
-
试剂盒组成
本产品提供以下试剂或组分:
NEB # 名称 组分货号 储存温度 数量 浓度 -
E8210S Multi-temperature Ph.D™.-12 Phage Display Peptide Library Kit v2 E8210-1 -20 Ph.D.™-12 Phage Display Peptide Library E8111AVIAL -20 1 x 0.1 ml 1 x 1013 pfu/ml E. coli K12 ER2738 E4104SVIAL -20 1 x 0.2 ml Not Applicable -96 glll Sequencing Primer (20-mer) S1259AAVIAL -20 1 x 0.05 ml 10 pmol/μl DYKDDDDK Mouse mAb E8004AVIAL -20 1 x 0.015 ml Not Applicable Protein G Magnetic Beads S1430V 4 Protein G Magnetic Beads S1430AVIAL 4 1 x 0.15 ml Not Applicable
-
-
优势和特性
Features
- 即用型复杂噬菌体库;表型与基因型之间的内在关联支持在单个微孔板或 Eppendorf 试管中筛选数十亿个克隆
- 对照淘选实验无需执行封闭步骤,可避免噬菌体与塑料结合物发生非特异性结合
- 使用 Protein G 磁珠进行对照淘选实验,可减少繁琐的板/孔冲洗步骤
- 随机区域的长度(12-mer)便于形成分子内二级结构,并在结合位点之间留出序列间隙
- 无需使用辅助噬菌体进行扩增
- 利用简单明了的分子生物学和无菌培养技术,可在不到一周的时间内获得肽结合序列
- 提供的 -96 gIII 测序引物(500 pmol)可进行 50 次以上测序反应
-
相关产品
相关产品
- Ph.D.™ 多肽展示克隆系统
- PhD-7 噬菌体展示肽库试剂盒 v2
- PhD-C7C 噬菌体展示肽库试剂盒 v2
单独销售的组分
- Ph.D.™-12 噬菌体展示肽库
- e4104-ecoli-k12-er2738
- Protein G 磁珠
-
注意事项
- 若要长期贮存(> 30 天)E. coli K12 ER2738,推荐贮存于 -80℃。
- Protein G 磁珠应贮存于 4℃,以防冻坏。
- 初代试剂盒(NEB #E8110)和二代试剂盒(简称 v2;NEB #E8210)均包含相同的 Ph.D.-12 噬菌体展示肽库组份(NEB #E8111)。
- M13 兼容大多数缓冲液条件;不过,洗脱缓冲液可能受制于扩增大肠杆菌所需的培养条件。如果使用二代测序方式,则无需通过扩增来富集噬菌体池。浏览现有文献了解操作流程。
- 提供的 -96 gIII 测序引物(500 pmol)可进行 50 次以上测序反应。
-
参考文献
- Sidhu, S.S. (2000). Curr. Opin. Biotechnol.. 11, 610-616.
- Rodi, D.J. and Makowski, L. (1999). Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. . 10, 87-93.
- Wilson, D.R. and Finlay, B.B. (1998). Can. J. Microbiol.. 44, 313-229.
- Parmley, S.F. and Smith, G.P. (1998). Gene. 73, 305-313.
- Scott, J.K. and Smith, G.P. (1990). Science. 249, 386-390.
- Whaley, S.R. et al. (2000). Nature. 405, 665-668.
- Noren, K.A. and Noren, C.J. (2001). Methods. 23, 169-178.
- Rozinov, M.N. and Nolan, G.P (1998). Chem. Biol.. 5, 713-728.
- Rodi, D.J. et al. (1999). J. Mol. Biol.. 285, 197-203.
操作说明、说明书 & 用法
-
操作说明
- Quick Start Protocol PhD Phage Display Peptide Library Kit v2
- Panning Protocol 1: Solution-phase Panning with Affinity Bead Capture
- Panning Protocol 2: Surface-Phase Panning (Direct Target Coating)
- Phage ELISA Binding Assay with Direct Target Coating
- Phage Titering
- Plaque Amplification for ELISA Samples
- Post Panning Protocol 1: Rapid Purification of Single-Stranded DNA Templates for Sequencing Reactions
-
说明书
产品说明书包含产品使用的详细信息、产品配方和质控分析。- manualE8210_E8211_E8111_E8212
-
应用实例
- Ph.D.™ Peptide Display Cloning System
FAQs & 问题解决指南
-
FAQs
- What is the difference between the original and version 2 (v2) Phage Display kits?
- Which of the three ready-made libraries should I choose?
- What is the difference between the three ready-made libraries?
- Can a different bacterial strain be used with the Ph.D.™ Phage Display?
- No plaques are visible when titering using a Ph.D.™ Phage Display Library.
- I am using Ph.D.™ Phage display and the amplified phage titer is low.
- I am using Ph.D.™ Phage Display and the phage DNA templates do not yield a readable sequence.
- I am using Ph.D.™ Phage Display and the sequencing templates do not run where they should on a gel.
- I am using Ph.D.™ Phage Display and after 4 or more rounds of panning all clones are wild-type phage (white plaques).
- When performing an experiment using Ph.D.™ Phage Display, the ELISA indicates that background binding to the plate is as high as binding to the target.
- When using the Ph.D.™ Phage Display, panning yielded a consensus sequence, but no ELISA signal.
- Where can I find references for Ph.D.™ phage display libraries?
-
问题解决指南
- Phage Display Troubleshooting Guide (NEB #E8210, #E8211, #E8212)
