上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理New England Biolabs(NEB)酶试剂全线产品,欢迎访问官网了解更多产品信息和订购。
产品信息
经基因工程改造的大肠杆菌(E. coli)化学感受态 B 细胞,可在细胞质中表达含有二硫键的蛋白。
重点
- 经过基因工程改造的大肠杆菌(E. coli)B 菌株,可促进细胞质中二硫键的形成
- 组成性表达二硫键异构酶 DsbC 的染色体拷贝
- DsbC 促进错误氧化蛋白纠正为正确形式(1、3)
- 细胞质 DsbC 也是一种分子伴侣,有助于不需二硫键的蛋白折叠(4)
- BL21 源增强型菌株
- 消除了非特异性核酸内切酶 I(endA1)的活性,以获得最高质量的质粒制备
- Lon 和 OmpT 蛋白酶缺失
- 抗 T1 噬菌体(fhuA2)、Nit、Spec、Str*
*可能观察到对低水平的链霉素存在抗性。
基因型
fhuA2 [lon] ompT ahpC gal λatt::pNEB3-r1-cDsbC (SpecR, lacIq) ΔtrxB sulA11 R(mcr-73::miniTn10–TetS)2 [dcm] R(zgb-210::Tn10 –TetS) endA1 Δgor ∆(mcrC-mrr)114::IS10
- 产品类别:
- SHuffle Expression,
- E. coli Protein Expression Strains Products,
- Protein Expression Products,
E. coli Expression Strains Products
- 应用:
- T7 Expression,
- Expression of Difficult Proteins,
- Disulfide-bonded Protein Expression,
- Protein Expression in E. Coli,
Protein Expression
-
产品组分信息
本产品提供以下试剂或组分:
NEB # 名称 组分货号 储存温度 数量 浓度 -
C3028J -80 SHuffle® Express Competent E. coli C3028JVIAL -80 12 x 0.05 ml Not Applicable
-
-
特性和用法
Antibiotic for Plasmid Selection
用于质粒筛选的抗生素 使用浓度 Ampicillin 100 µg/ml Carbenicillin 100 µg/ml Chloramphenicol 33 µg/ml Kanamycin 30 µg/ml Tetracycline 15 µg/ml 货运单
- Ships on dry ice
抗生素耐药性
- str(可能观察到对低水平的链霉素存在抗性)
- nit
- spec
-
优势和特性
Features
- 蛋白酶缺失/B 菌株
- 在细胞质中正确折叠具有多个二硫键的蛋白的能力更强
应用特性
图 1:粗裂解物 vtPA 活性测定: 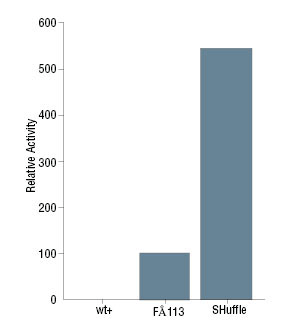
截短型组织纤溶酶原激活剂(vtPA),表达自大肠杆菌(E. coli)细胞质的 pTrc99a 质粒,当正确折叠和氧化时包含 9 个二硫键。诱导后收集细胞并制备粗细胞裂解物。使用显色底物 Chromozym t-PA(Roche #11093037001)测定 vtPA 活性,并使用 Bradford 试剂进行蛋白浓度测定。大肠杆菌(E. coli)wt+ 细胞为 DHB4,是 FÅ113(Origami™)的亲本。 图 2:从粗裂解物测定的 PfCHT1 几丁质酶活性: 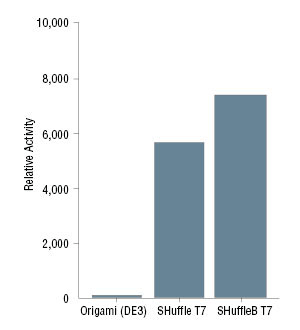
在 T7 启动子调控下,表达自质粒的恶性疟原虫几丁质酶(PfCHT1)含三个半胱氨酸。诱导后收集细胞并制备粗细胞裂解物。使用显色底物(CalBioChem #474550)测定 PfCHT1 活性,并使用 Bradford 试剂进行蛋白浓度测定。 -
相关产品
相关产品
- SOC Outgrowth 培养基
- SHuffle® T7 E. coli 感受态细胞
- SHuffle® T7 表达 E. coli 感受态细胞
- SHuffle® T7 表达 lysY E. coli 感受态细胞
-
注意事项
- 贮存和处理:感受态细胞应在 -80℃ 下贮存。在 -20℃ 贮存会导致转化效率显著降低。当细胞温度高于 -80℃ 时,即使不融化,细胞也会失去效率。
-
参考文献
- Bessette, P.H. et al. (1999). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 96, 13703-13708.
- Qiu, J., Swartz, J.R. and Georgiou, G. (1998). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64, 4891-4896.
- Levy, R. et al. (2001). Protein Expr. Purif. 20, 338-347.
- Chen, J. et al. (1999). J. Biol. Chem. 274, 19601-19605.
- Boyd, D. et al. (2000). J. Bacteriol. 182, 842-847.
- de Marco, A. (2009). Microbial Cell Factories. 8, 26.
操作说明、说明书 & 用法
-
操作说明
- Expression Using SHuffle (C3028)
- Transformation Protocol (#C3029, #C3026, #C3028 and #C3030)
-
使用指南
- Additional E. coli Strain Genotypes
- Genetic Markers
- McrA, McrBC and EcoKI Strain Phenotypes
-
应用实例
- Transformation of SHuffle® Competent Cell Strains
工具 & 资源
-
选择指南
- Characteristics of Select E.coli Strains
- Competent Cell Product Comparison
- Competent Cell Selection Guide
- SHuffle® Strain Selection Chart
FAQs & 问题解决指南
-
FAQs
- What are the strain properties (C3028)?
- What applications are SHuffle® strains useful for?
- Does my protein have disulfide bonds?
- Which SHuffle® strain should I use?
- Is there anything I can do to increase protein yield when using SHuffle strains?
- What are the growth characteristics of the SHuffle strains?
- How do SHuffle® strains aid in cytoplasmic disulfide bond formation?
- Can I store competent cells at -20°C instead of -80°C?
- How should I express my protein of interest in SHuffle?
- Does Streptomycin and/or Spectinomycin need to be added when growing SHuffle strains?
- Can I conduct M13 phage display experiments in SHuffle strains?
- Can I conduct blue/white screening using alpha complementation of lacZ in SHuffle strains?
- Which SHuffle strains are resistant to chloramphenicol? Is chloramphenicol required for maintenance of the mini F plasmid?
- Do SHuffle cells grow in minimal media?
- Are SHuffle strains temperature sensitive?
- Is the genome of SHuffle strains available?
- Can one use SHuffle cells to secrete my protein of interest?
