上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理New England Biolabs(NEB)酶试剂全线产品,欢迎访问官网了解更多产品信息和订购。
产品信息
PURExpress 文献引用
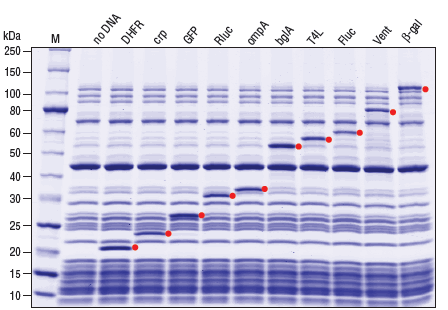
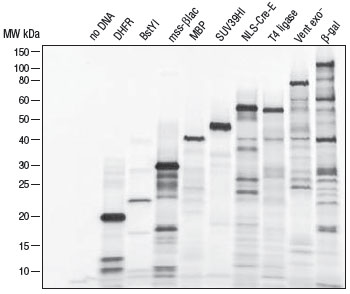
- 产品类别:
- PURExpress,
- Cell-Free Protein Expression Products,
- Protein Expression Products
- 应用:
- PURExpress,
- Toxic Protein Expression,
- Cell-Free Protein Expression,
- High-throughput cloning and automation solutions,
- Expression of Difficult Proteins,
- Disulfide-bonded Protein Expression,
Protein Expression
-
试剂盒组成
本产品提供以下试剂或组分:
NEB # 名称 组分货号 储存温度 数量 浓度 -
E6800S -80 PURExpress Solution A B0228AVIAL -80 1 x 0.1 ml 2.5 X Solution B (75 μl) P0760AVIAL -80 1 x 0.075 ml Not Applicable PURExpress Control DHFR Plasmid N0424AVIAL -20 1 x 0.01 ml 125 ng/µl
-
E6800L -80 PURExpress Solution A B0228AVIAL -80 10 x 0.1 ml 2.5 X Solution B (75 μl) P0760AVIAL -80 10 x 0.075 ml Not Applicable PURExpress Control DHFR Plasmid N0424AVIAL -20 1 x 0.01 ml 125 ng/µl
-
-
优势和特性
应用特性
- 快速合成用于蛋白质特性研究的分析量级别的样本
- 确认开放阅读框
- 检测突变对 ORF 的影响
- 合成具有活性和功能域的截短蛋白
- 掺入修饰的、非天然的或标记的氨基酸
- 绘制抗原表位图谱
- 毒性蛋白表达
- 核糖体展示
- 翻译和/或蛋白折叠研究
- 体外区域化
-
相关产品
相关产品
- PURExpress® Δ (aa, tRNA) 试剂盒
- PURExpress® Δ RF123 试剂盒
- 小鼠 RNase 抑制剂
- PURExpress® Δ Ribosome 试剂盒
- E. coli 核糖体
- PURExpress® 二硫键增强剂
-
注意事项
- 提供 125 ng/µl 的对照(DHFR)模板。使用 2 µl 模板进行阳性对照反应。模板 DNA,特别是通过质粒小提制备的 DNA(如 Qiagen)通常是 RNase 酶污染的主要来源。我们强烈建议在每个反应中加入 20 单位的小鼠 RNase 抑制剂(NEB #M0314)。
- PURExpress DHFR 对照模板序列文件:Fasta GenBank
- 贮存条件:试剂盒所有组份必须贮存于 -80℃。
- 将溶液 B 加入溶液 A 中,不要在未缓冲的情况下稀释溶液 B。我们建议 25 μl 反应体系中模板 DNA 的起始量为 250 ng。可以通过建立多个反应并滴定加入不同起始量的 DNA,来确定模板 DNA 的最佳用量。通常情况下,每 25 μl 反应体系中,模板 DNA 最佳用量范围在 25 – 1000 ng 之间。
-
参考文献
- Asahara, H. and Chong, S. (2010). In vitro genetic reconstruction of bacterial transcription initiation by coupled synthesis and detection of RNA polymerase holoenzyme. Nuc.Acid. Res.
- Desai, Bijoy J., Yuki Goto, Alessandro Cembran, Alexander A. Fedorov, Steven C. Almo, Jiali Gao, Hiroaki Suga, and John A. Gerlt (2014). Investigating the role of a backbone to substrate hydrogen bond in OMP decarboxylase using a site-specific amide to ester substitution. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 201411772.
- Gu, Liangcai, Chao Li, John Aach, David E. Hill, Marc Vidal, and George M. Church (2014). Multiplex single-molecule interaction profiling of DNA-barcoded proteins. Nature.
- Gupta, Pulkit, Shanmugapriya Sothiselvam, Nora Vázquez-Laslop, and Alexander S. Mankin (2013). Deregulation of translation due to post-transcriptional modification of rRNA explains why erm genes are inducible. Nature communications. 4,
- Kaiser, Christian M., Daniel H. Goldman, John D. Chodera, Ignacio Tinoco, and Carlos Bustamante (2011). The ribosome modulates nascent protein folding. Science. 334 (6063), 1723-1727.
- Nakagawa, So, Stephen S. Gisselbrecht, Julia M. Rogers, Daniel L. Hartl, and Martha L. Bulyk (2013). DNA-binding specificity changes in the evolution of forkhead transcription factors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 110(30), 12349-12354.
- Ramadoss, Nitya S., John N. Alumasa, Lin Cheng, Yu Wang, Sharon Li, Benjamin S. Chambers, Hoon Chang et al (2013). Small molecule inhibitors of trans-translation have broad-spectrum antibiotic activity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 110(25), 10282-10287.
- Rosenblum, Gabriel, and Barry S. Cooperman (2014). Engine out of the chassis: Cell-free protein synthesis and its uses. FEBS letters. 588(2), 261-268.
- Stafford, Ryan L., Marissa L. Matsumoto, Gang Yin, Qi Cai, Juan Jose Fung, Heather Stephenson, Avinash Gill et al (2014). In vitro Fab display: a cell-free system for IgG discovery. Protein Engineering Design and Selection. 27(4), 97-109.
- Tuckey, Corinna, Haruichi Asahara, Ying Zhou, and Shaorong Chong (2014). Protein Synthesis Using a Reconstituted Cell‐Free System. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. 16-31.
- Weirauch, Matthew T., Atina Cote, Raquel Norel, Matti Annala, Yue Zhao, Todd R. Riley, Julio Saez-Rodriguez et al (2013). Evaluation of methods for modeling transcription factor sequence specificity. Nature biotechnology. 31(2), 126-134.
- Noto, T., Kurth, H., Kataoka, K., Aronica, L., DeSouza, L., Siu, K., Pearlman, R., Gorovsky, M. and Mochizuki, K. (2010). The tetrahymena argonaute-binding protein Giw1p directs a mature argonaute-siRNAcomplex to the nucleus. Cell. 140, 692-703.
- Tanner, D., Cariello, D., Woolstenhulme, C., Broadbent, M. and Buskirk, A. (2009). Genetic identification of nascent peptides that induce ribosome stalling. J. Biol.Chem. 284, 34809-34818.
- Talabot-Ayer, D., Lamacchia, C., Gabay, C., and Palmer, G. (2009). Interleukin-33 is biologically activeindependently of Caspase-1 cleavage. J. Biol.Chem. 284, 19420-19426.
- Feng, Y. and Cronan, J. E. (2009). A new memberof the Eschericia coli fad regulon: transcriptional regulation offadM (ybaW). J.Bacteriol. 191, 6320-6328.
- Solaroli, N., Panayiotou, C., Johansson, M., and Karlsson, A. (2009). Identification of two active functional domains of human adenylate kinase 5. FEBSLett. 283, 2872-2876.
- Arenz, Stefan, Haripriya Ramu, Pulkit Gupta, Otto Berninghausen, Roland Beckmann, Nora Vázquez-Laslop, Alexander S. Mankin, and Daniel N. Wilson (2014). Molecular basis for erythromycin-dependent ribosome stalling during translation of the ErmBL leader peptide. Nature communications. 5,
- Chong, Shaorong (2014). Overview of Cell‐Free Protein Synthesis: Historic Landmarks, Commercial Systems, and Expanding Applications. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. 16-30.
- Daugherty, Ashley B., Sridhar Govindarajan, and Stefan Lutz (2013). Improved Biocatalysts from a Synthetic Circular Permutation Library of the Flavin-Dependent Oxidoreductase Old Yellow Enzyme. Journal of the American Chemical Society . 334 (38), 14425-14432.
操作说明、说明书 & 用法
-
操作说明
- Protein Synthesis Reaction using PURExpress (E6800)
- Analysis of Synthesized Protein using PURExpress (E6800)
- Determination of Protein Synthesis Yield with PURExpress (E3313, E6800, E6840, E6850)
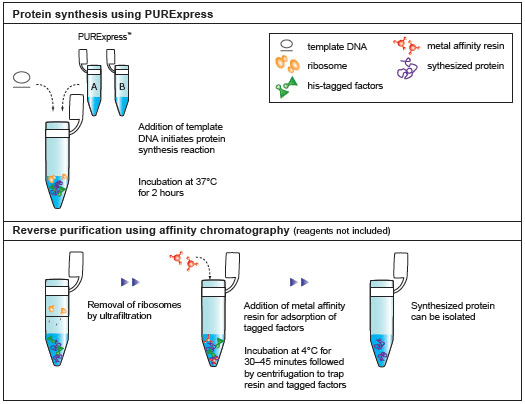
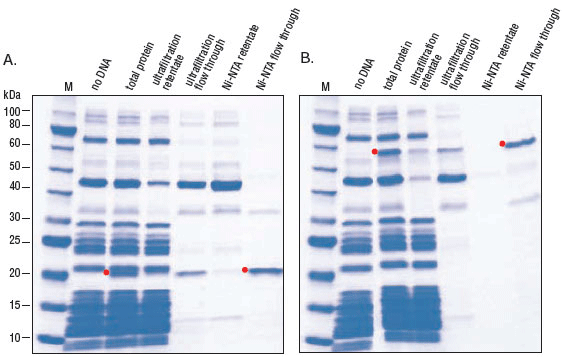
- Purification of Synthesized Protein using Reverse His-tag Purification
- Measurement of 35S-Methionine Incorporation by TCA Precipitation and Yield Determination using PURExpress
-
说明书
产品说明书包含产品使用的详细信息、产品配方和质控分析。- manualE6800_E3313_E6840_E6850
-
应用实例
- Use of the PURExpress® in vitro Protein Synthesis Kit, Disulfide Bond Enhancer and SHuffle® Competent E. coli for heterologous in vitro and in vivo cellulase expression.
- Scaling down to scale up Miniaturizing cell free protein synthesis reactions with the Echo 525 Acoustic Liquid Handler
工具 & 资源
-
选择指南
- Protein Expression and Purification Selection Chart
- PURExpress® vs. NEBExpress® Application Chart
FAQs & 问题解决指南
-
FAQs
- When using PURExpress, I was unable to synthesize the control protein?
- When using PURExpress, I was able to synthesize the control protein, but the target sample is not present or present in low yield?
- When using PURExpress, I was able to synthesize the target protein, but full-length product is not major species?
- Where can I find many more detailed FAQs for PURExpress?
- Are there PURExpress citations?
-
实验技巧
- 在冰上融化试剂和建立反应体系
使用前,请将溶液 A 和 B 充分混合。不要涡旋溶液 B 或核糖体,将其轻轻混合。
溶液 A 可能呈浑浊白色。以均匀悬浮状态加入到反应中。
在冰上按下列加样顺序建立反应体系:溶液 A、溶液 B、RNAse 抑制剂、水、模板 DNA 或 RNA
建立反应体系后,要确保所有试剂都充分混合,可以轻柔地上下吸打混匀并进行短暂瞬时离心,37℃条件下温育 2 到 4 小时。 - 在冰上融化试剂和建立反应体系
